Pengaturcaraan neuro-linguistik, satu kaedah yang digunakan untuk komunikasi interpersonal, perubahan organisasi dan psikoterapi yang digunakan untuk membantu rakyat mengubah tingkah laku mereka
Pengaturcaraan neuro-linguistik (NLP) adalah satu pendekatan untuk komunikasi, perkembangan peribadi, dan psikoterapi yang diwujudkan pada tahun 1970-an. Tajuk merujuk kepada sambungan dinyatakan antara proses neurologi ("neuro"), bahasa ("bahasa") dan corak tingkah laku yang telah dipelajari melalui pengalaman ("pengaturcaraan") dan boleh diadakan untuk mencapai matlamat tertentu dalam life.According kepada neuroscientists tertentu, ahli psikologi dan ahli bahasa, nlp tidak disokong oleh bukti saintifik semasa, dan menggunakan terma-terma dan konsep yang salah dan mengelirukan.
Pengasas NLP, Richard Bandler dan John Grinder, mengatakan bahawa NLP mampu menangani masalah seperti fobia, kemurungan, tabiat gangguan, penyakit psikosomatik dan gangguan pembelajaran. [Perlu petikan] matlamat yang dinyatakan mereka adalah dalam "mencari jalan untuk membantu orang mempunyai kehidupan yang lebih baik, penuh dan kaya. " Bandler dan Grinder mendakwa bahawa jika corak berkesan tingkah laku orang yang luar biasa boleh dimodelkan maka pola-pola ini boleh diperoleh oleh orang lain. NLP telah diterima pakai oleh ahli-ahli terapi swasta, termasuk hypnotherapists [citation needed],
dan dalam pengurusan bengkel dan seminar yang dikatakan kepada perniagaan dan kerajaan
Techniques or set of practices This section requires expansion.
According to one study by Steinbach (1984), a classic interaction in NLP can be understood in terms of several major stages including establishing rapport, gathering information about a problem state and desired goals, using specific tools and techniques to make interventions, and integrating proposed changes into the client's life. The entire process is guided by the non-verbal responses of the client. The first is the act of establishing and maintaining rapport between the practitioner and the client which is achieved through pacing and leading the verbal (e.g. sensory predicates and keywords) and non-verbal behaviour (e.g. matching and mirroring non-verbal behavior, or responding to eye movements - see chart) of the client.
An "eye accessing cue chart" as it appears as an example in Bandler & Grinder's Frogs into Princes (1979)
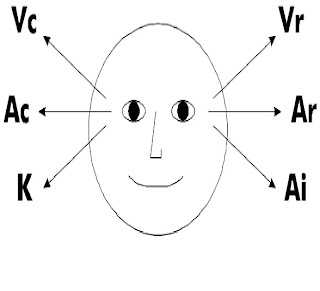
Once rapport is established, the practitioner may gather information (e.g. using the meta model questions) about the client's present state as well as help the client define a desired state or goal for the interaction. The practitioner pays particular attention to the verbal and non-verbal responses as the client defines the present state and desired state and any resources that may be required to bridge the gap. The client is typically encouraged to consider the consequences of the desired outcome may have on his or her personal or professional life and relationships, taking into account any positive intentions of any problems that may arise (i.e. ecological check).Fourth, assisting the client in achieving the desired outcomes by using certain tools and techniques to change internal representations and responses to stimuli in the world. Other tools and techniques include indirect suggestion from the Milton model, reframing, and submodalities. Finally, the changes are "future paced" by helping the client to mentally rehearse and integrate the changes into his or her life. For example, the client may be asked to "step into the future" and represent (mentally see, hear and feel) what it is like having already achieved the outcome.
According to Stollznow (2010), "NLP also involves fringe discourse analysis and “practical” guidelines for “improved” communication. For example, one text asserts “when you adopt the “but” word, people will remember what you said afterwards. With the “and” word, people remember what you said before and after”.
No comments:
Post a Comment